How Cube works with Steep
When using the Cube Semantic Layer integration, metrics are defined in code, using views, and are version-controlled in your Cube project. Steep then uses the Cube API to make your metrics available for all end users in Steep. Steep will not use its built-in semantic layer for these metrics, and will instead use Cube for definitions, query generation, and execution. Otherwise, everything works just like with native Steep metrics.
Tip
You can combine metrics from Cube with metrics defined natively in Steep. This can help you to iterate on new metrics definitions in a flexible way, while managing core metrics centrally in code.
Setting up Cube
To set up your Cube project, create Cubes, and define metrics using Views in Cube.
Don't have a Cube project yet?
Learn how to get started here (Cube docs)
1. Model your data in Cube
Model your data using cubes, joins, measures and dimensions.
Example of a simple orders cube:
cubes:
- name: orders
sql_table: orders
measures:
- name: total
description: "Total number of orders received"
sql: net_orders
type: sum
dimensions:
- name: created_at
sql: TIMESTAMP(created_at)
type: time
- name: country
sql: country
type: string
2. Define metrics using views
Important
- In order to be considered a metric, views must have only one time dimension.
- If the view has only one measure, the view itself is considered a metric.
- If the view has multiple measures, each measure will be considered a metric.
Example view that produces an orders_total metric in Steep.
views:
- name: orders_total
description: "Sum of total order amount. Includes tax and revenue."
includes:
# Measure
- orders.total
# Time
- orders.created_at
# Dimensions
- orders.country
- orders.segment
Learn more
Full reference to data modeling with Cube’s semantic layer Data modeling in Cube guide
3. Set metadata
Besides the core metric specification, it is possible to control some additional Steep metric properties from your Cube project using the meta field. This is optional and if not defined in your Cube project you can instead use the Steep UI to configure these properties for your metrics.
Currently supported properties are category_name (string), owner_emails (string array), is_private (boolean) and unlisted (boolean). You define these using the meta field of the view or measure.
- For single measure views the view's meta field will be used.
- For multi measure views the meta field of the measures will be used.
# Example
measures:
- name: registrations
...
meta:
category_name: Onboarding
owner_emails: [john@example.com]
is_private: false
unlisted: false
Tip
Fields can also be prefixes with steep_ eg. steep_category_name if you prefer vendor specific metadata fields or if you are already using those field names for other purposes.
Connect Cube to Steep
When you have set up your Cube project in Cube Cloud you need the REST API endpoint and API Secret for your setup in order to connect Steep to Cube. Log in to your Cube console and follow the steps below.
- REST API endpoint can be found on the Overview page
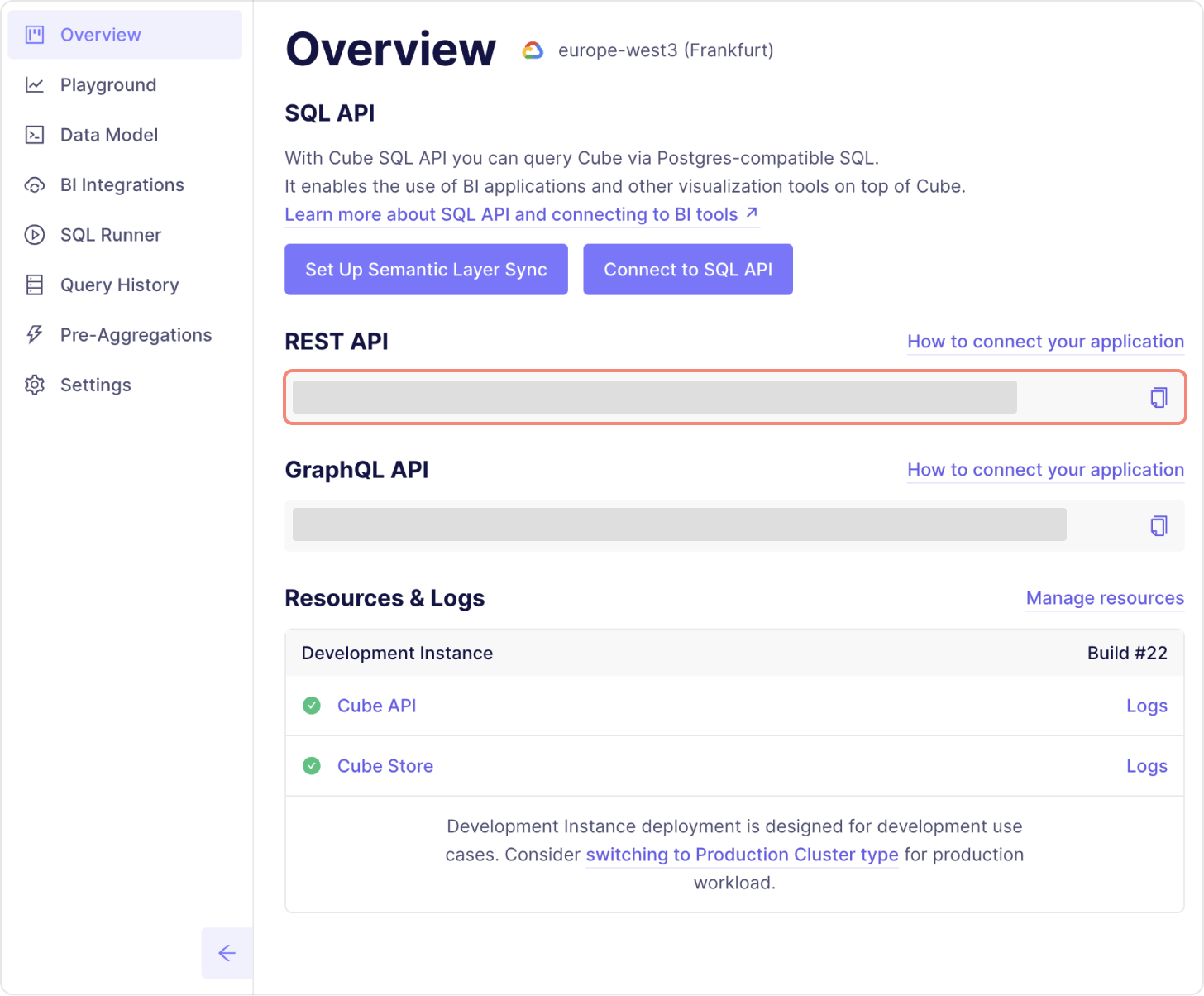
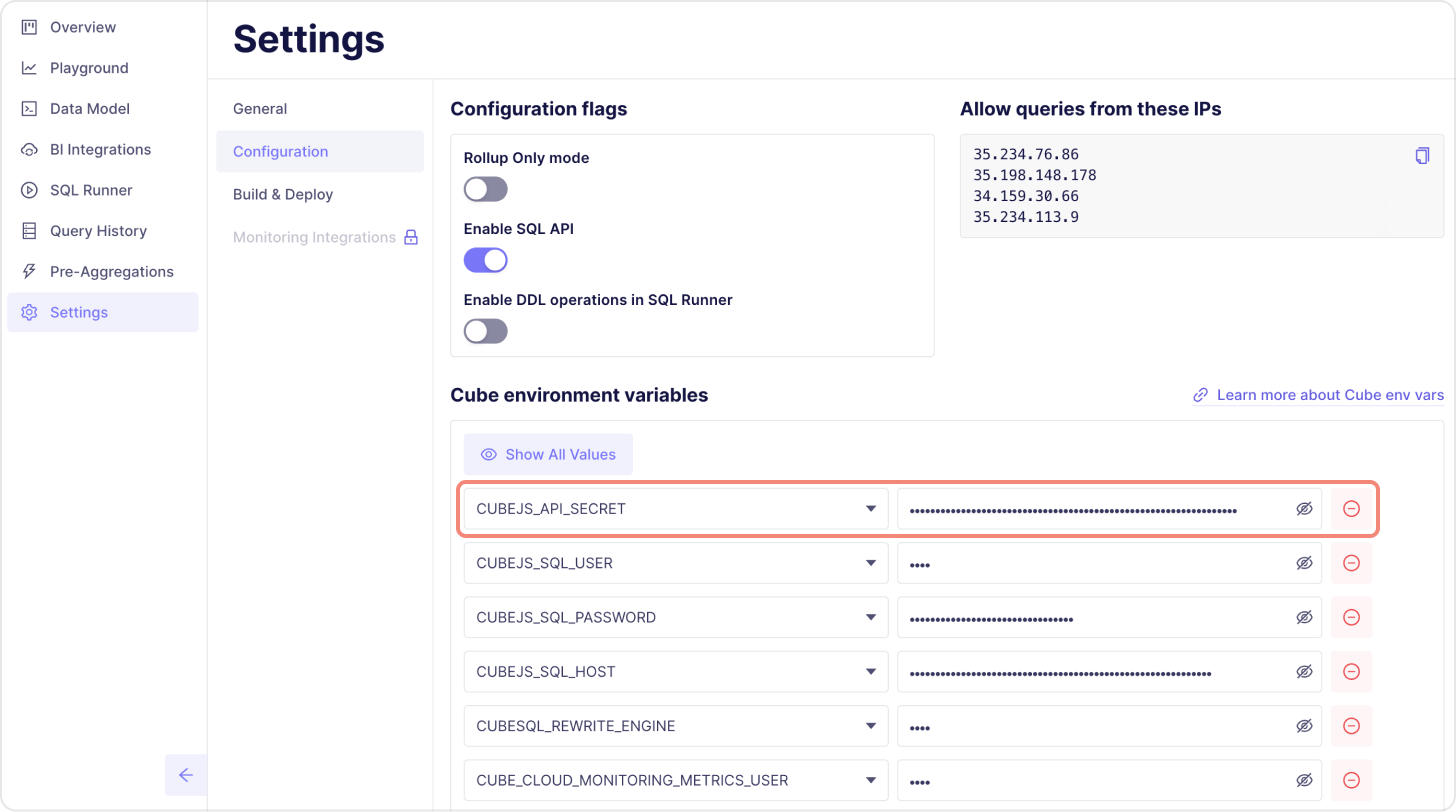
- API Secret can be found on the Settings / Configuration page under “Cube environment variables”. It’s named
CUBEJS_API_SECRET
- Copy the REST API endpoint and API Secret you got from Cube Cloud and paste it into Steep form for creating the Cube datasource
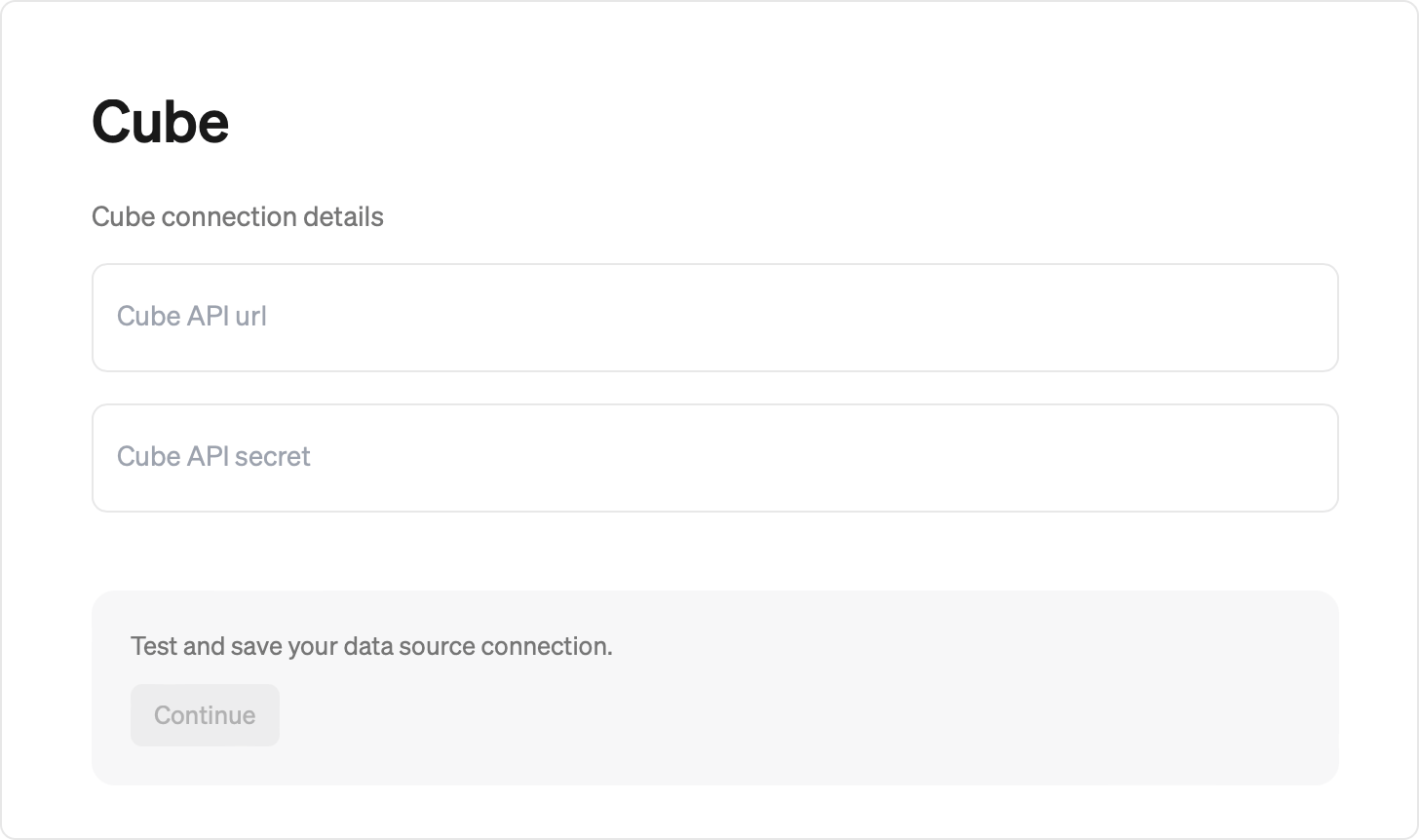
- Hit ‘Continue’ for your connection to be established and your Cube metrics to be synced into Steep. Done 🎉
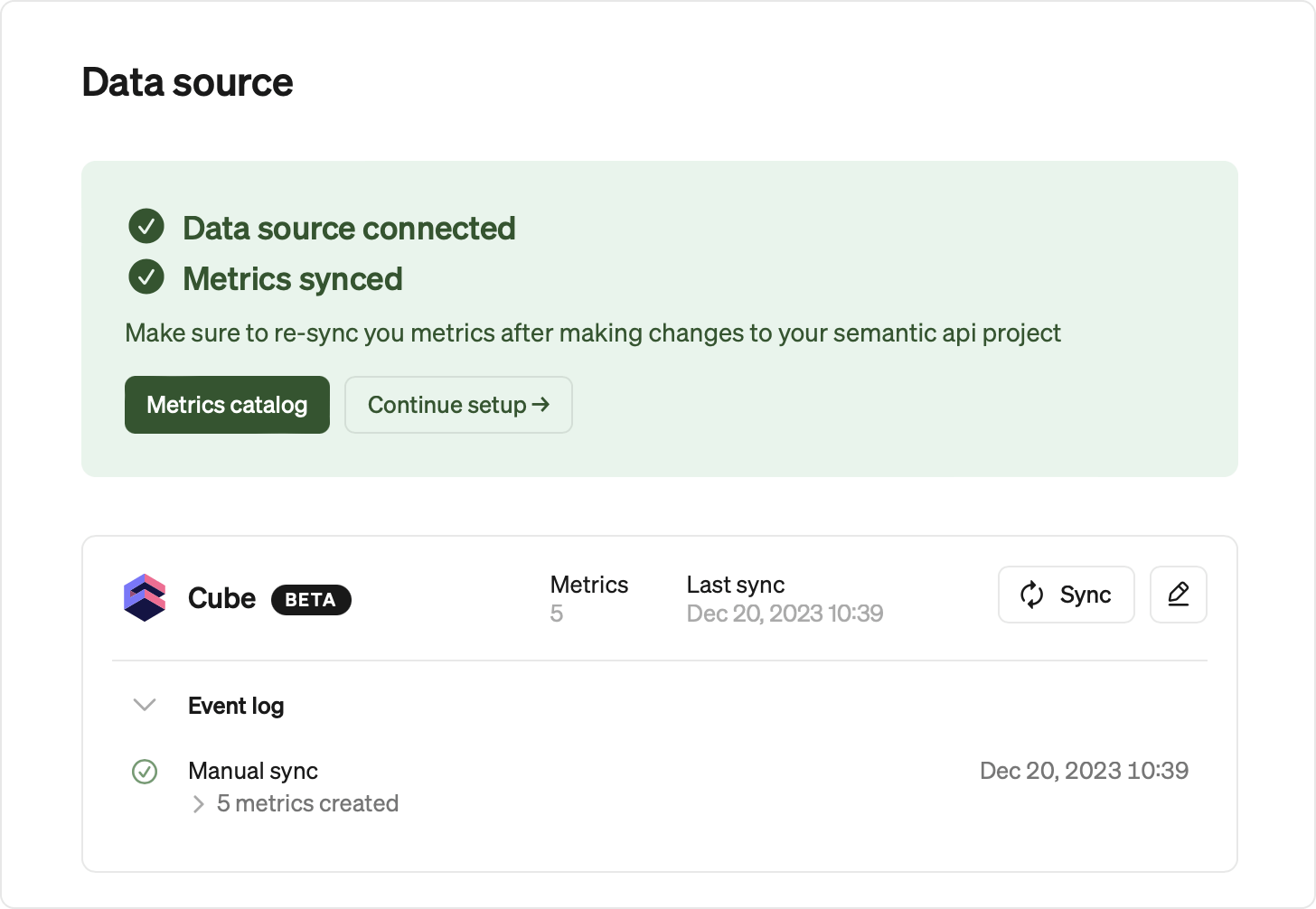
Syncing metrics from Cube to Steep
When first connecting, all Cube metrics will be synced to Steep. Views that have only one time dimension are considered to be a defined metric and will be picked up by Steep.
- If the view has only one measure the view itself is considered a metric.
- If the view has multiple measures, each measure will be considered a metric.
API sync
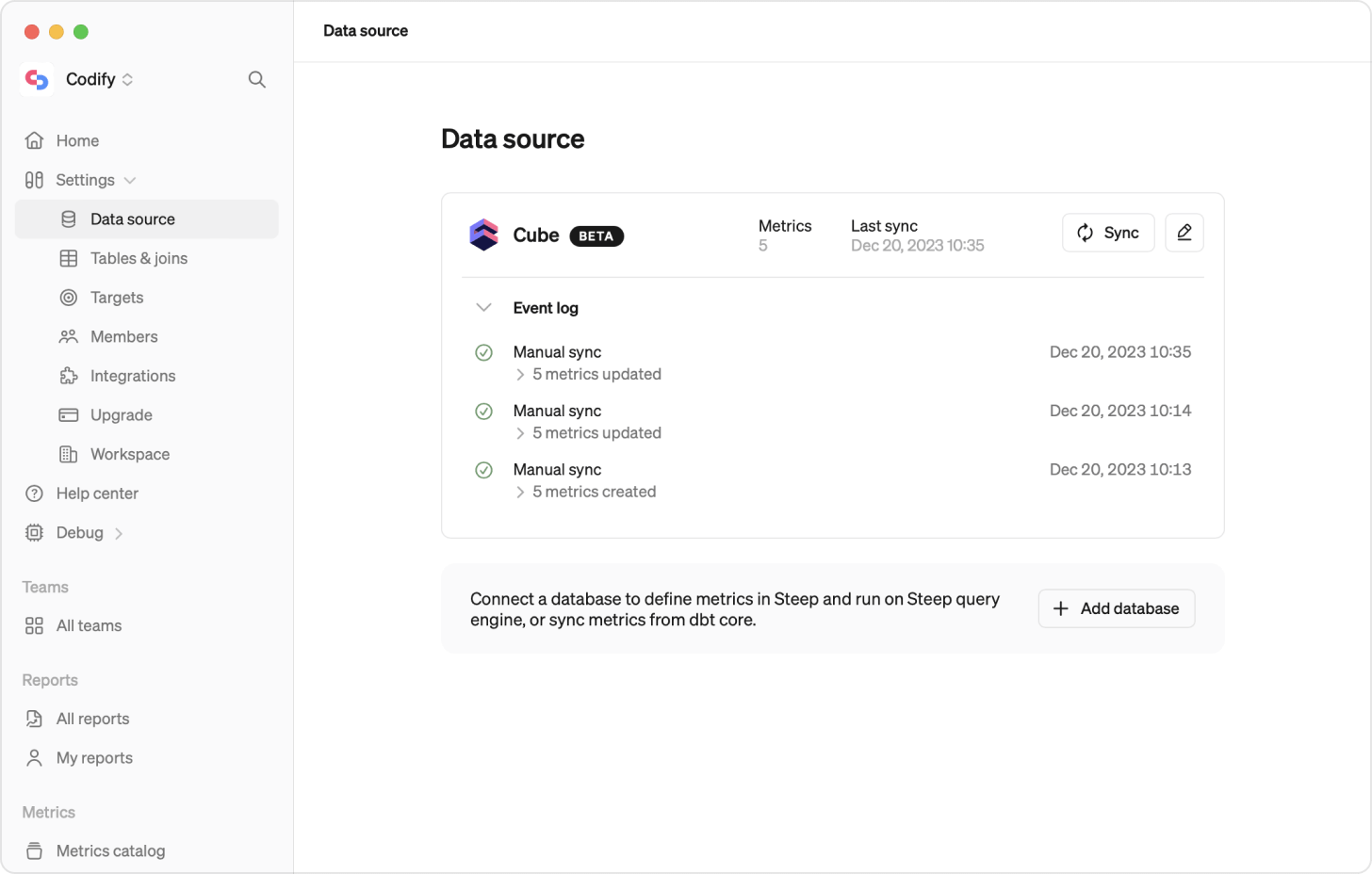
You can call an API endpoint at Steep to trigger a sync. This way you can automate the sync based on your needs by just integrating a call to Steep in your procees of updating metrics. Go to Settings / Data sources and expand the API sync section for detailed instructions on how to set it up.
Manual sync
Anytime you update a metric in your Cube Semantic Layer, you need to manually trigger a sync in Steep, on the Settings / Data sources page.